Questions
Below are optional practice problems for Quiz 1. These problems are intended to help you become more familiar with loops, functions, lists and dictionaries. Solutions for each problem can be found at the bottom of this page.
Lists T/F
- The values in a list cannot be changed while your program is running. (T/F)
- You can add, change, and remove items in a list. (T/F)
- For the purposes of this class, all items in a list are of the same type. (T/F)
- The first index of a list is 1. (T/F)
- The last index of a list is the length of the list. (T/F)
- You can initialize an empty list with no items. (T/F)
- To remove an item, you input the value of the item that you want to remove into the pop() function. (T/F)
- While loops inside a function may continue looping after a return statement is reached. (T/F)
- A while loop statement can you used anywhere you can write a statement. (T/F)
- You can put any kind of statement in the body of a while loop. (T/F)
Dictionaries T/F
- To access a value in a dictionary, you use the format
<dictionary_name>{key}. (T/F) - One value can be associated with multiple keys. (T/F)
- Dictionaries are mutable. In other words, the values in a dictionary can be changed after they are constructed. (T/F)
- Dictionaries can have lists or other dictionaries as their keys. (T/F)
- The
not inoperator can be used to check whether a specific key exists in a dictionary or not. (T/F) - For the purposes of this course, all values in a dictionary are of the same type. (T/F)
List Diagramming 1
Given the code listing below, draw an environment diagram then answer the questions that follow.
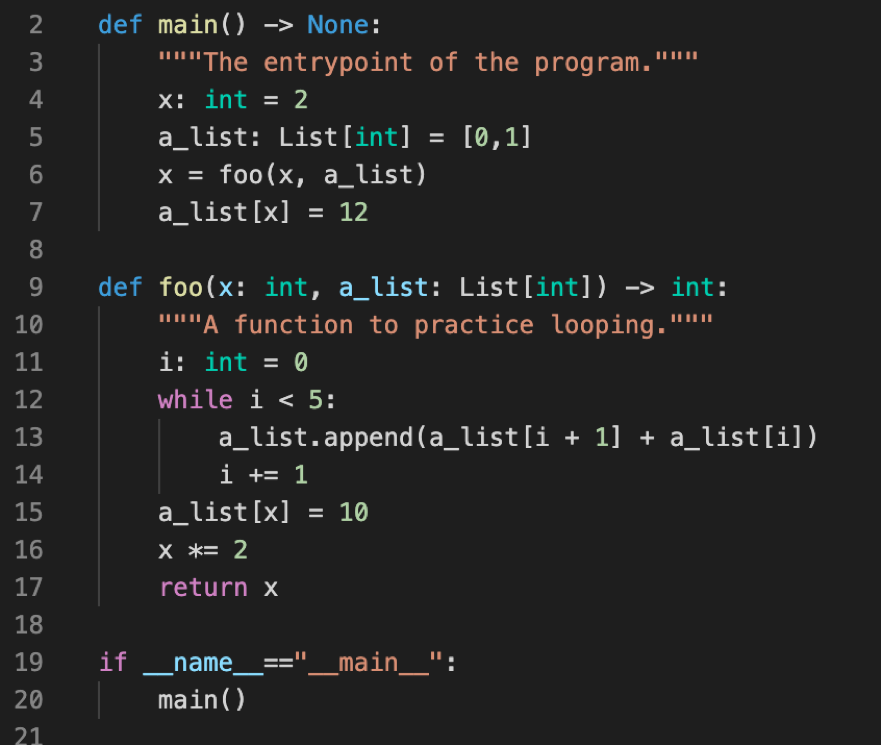
- What is the final value of
xin themainfunction frame? - What is the length of
a_listafter the code has finished running? - What are the final items in
a_list?
List Diagramming 2
Given the code listing below, draw an environment diagram then answer the questions that follow.
- From the
mainframe isb[2]defined? - From the
mainframe, what are the final items ina?
List Diagramming 3
Given the code listing below, draw an environment diagram then answer the question that follows.
- What is the final value of
iin the make_word frame?
Loops Diagramming 1
Given the code listing below, draw an environment diagram then answer the questions that follow.
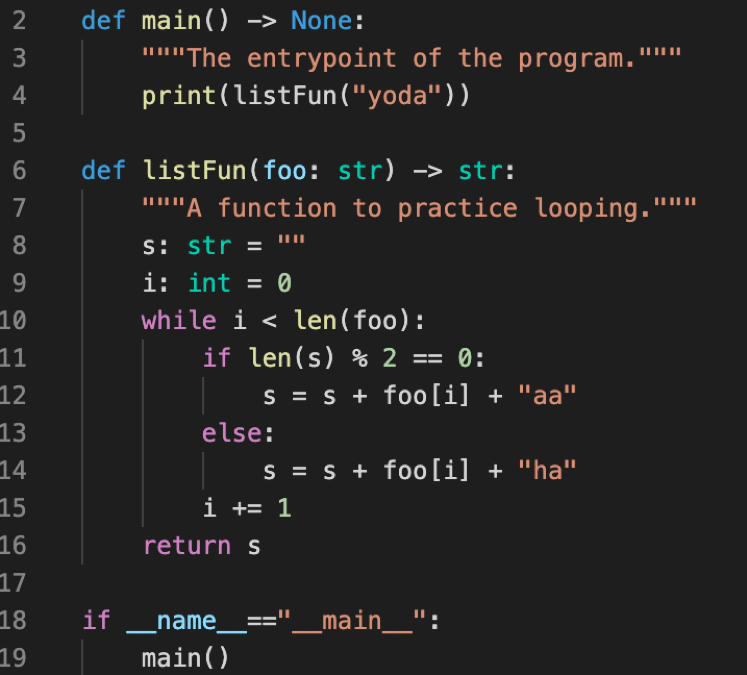
- What is the printed output?
- Write a function call to
listFunthat would return the value “saanhaoaawha”.
Dictionary Diagramming 1
Given the following code listing, draw an environment diagram.
Dictionary Diagramming 2
Given the following code listing, draw an environment diagram and answer the questions that follow.
- When
itemis incremented by1on line 9, isa_table["c"]mutated? - How many arrows come out of the
fillframe?
Function Writing 1
- Write a definition for a function called
reverse, which has one parameter of type str namedstringand returns a str that has all the characters ofstringin reverse order. Use a while loop. For example, a call toreversewith “hello” would return “olleh”.
Global Variables
Base your answers to the following questions on the code listing below.
- What is the printed output of this code listing?
- On line 8, the value of
xis changed. On what line isxdeclared? - Two different variables named
yare declared. What is the final value of the global variabley? - On line 11, a variable
yis changed. On what line is thisydeclared?
Solutions
Lists T/F
- F
- T
- T
- F
- F
- T
- F
- F
- T
- T
Dictionaries T/F
- F
- T
- T
- F
- T
- T
List Diagramming 1
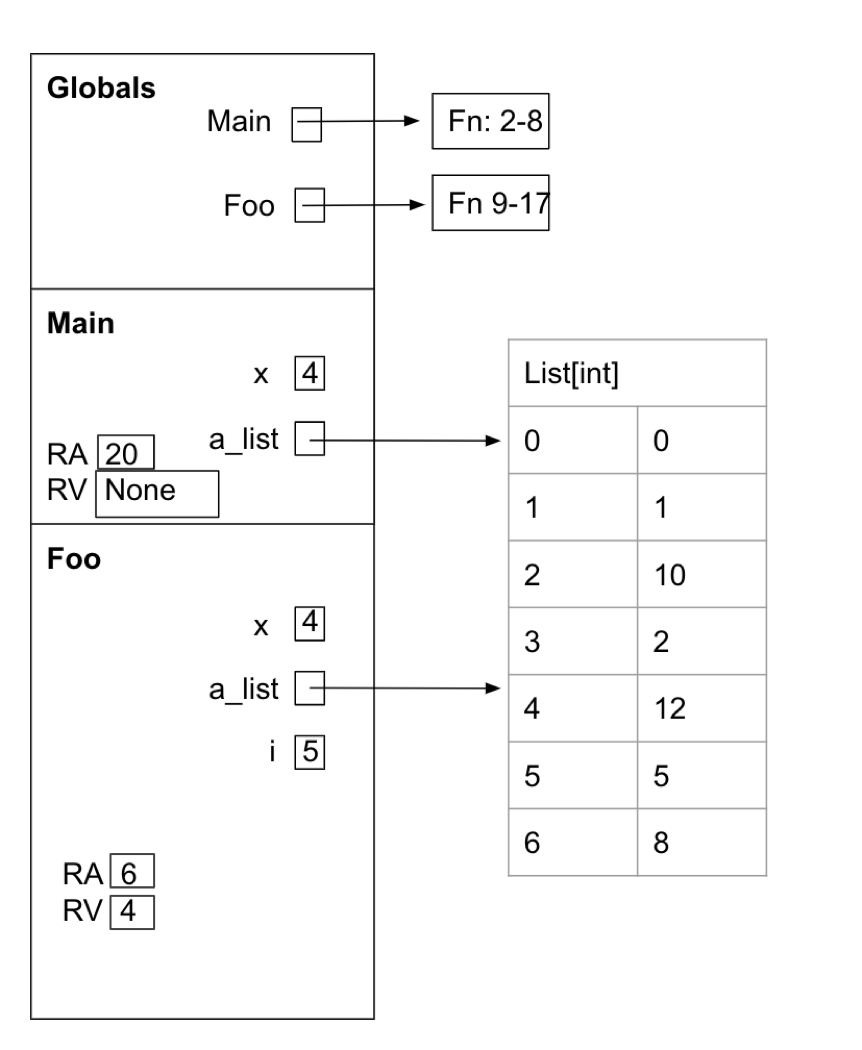
- 4
- 7
- [0, 1, 10, 2, 12, 5, 8]
List Diagramming 2
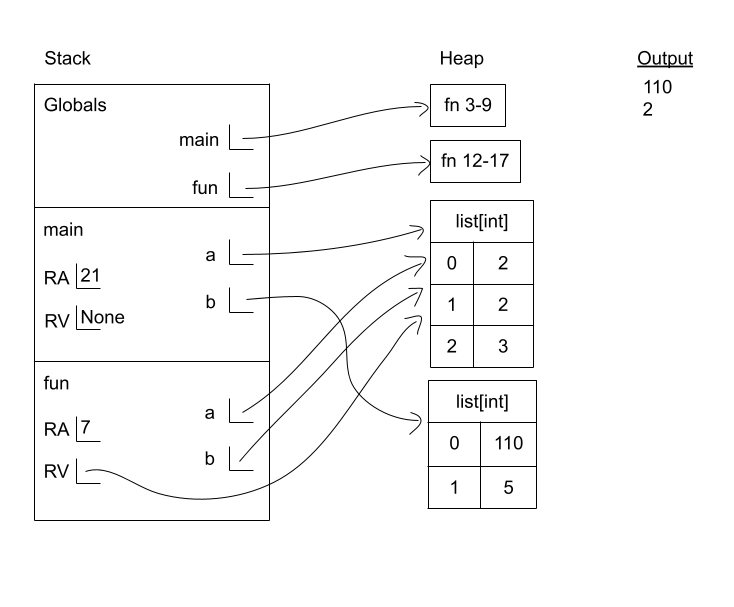
- No
- [2, 2, 3]
List Diagramming 3
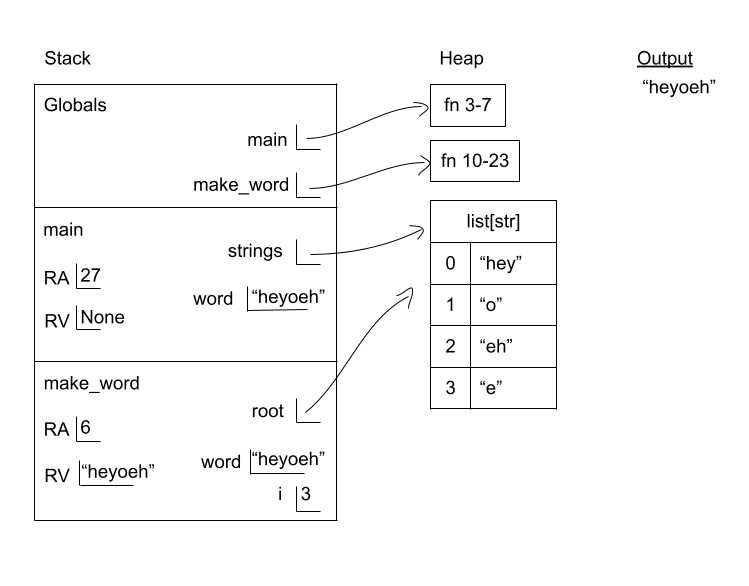
- 3
Loops Diagramming 1
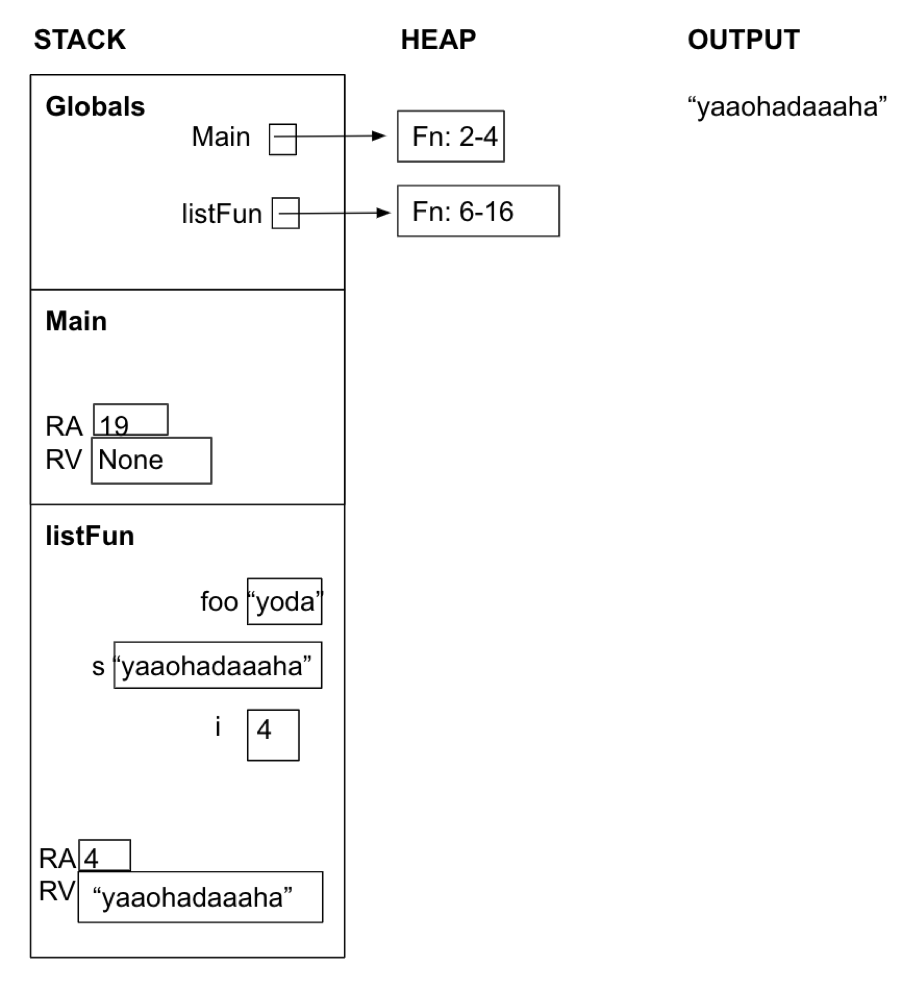
- “yaaohadaaaha”
- listFun(“snow”)
Dictionary Diagramming 1
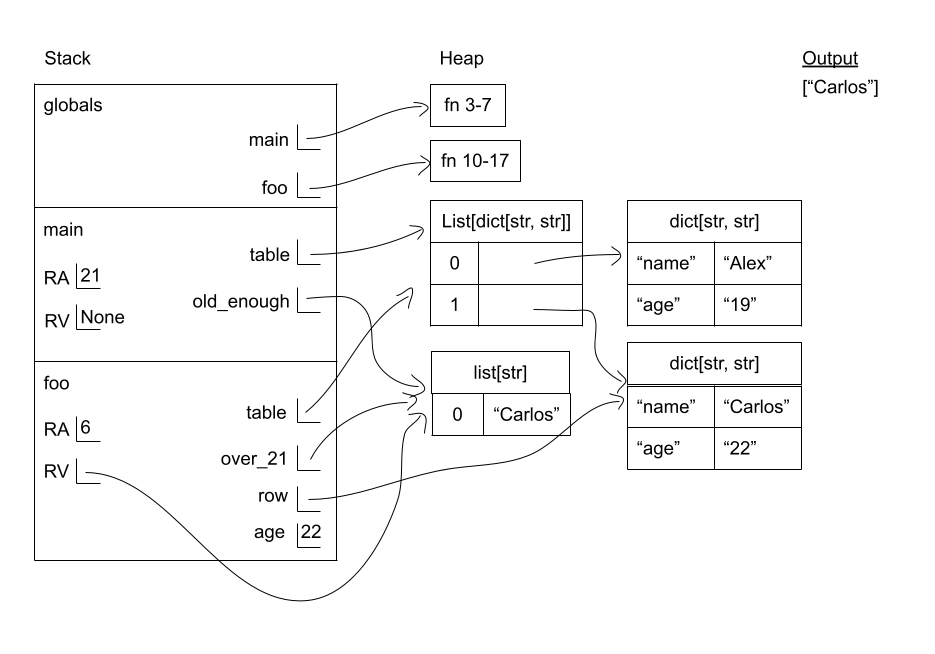
Dictionary Diagramming 2
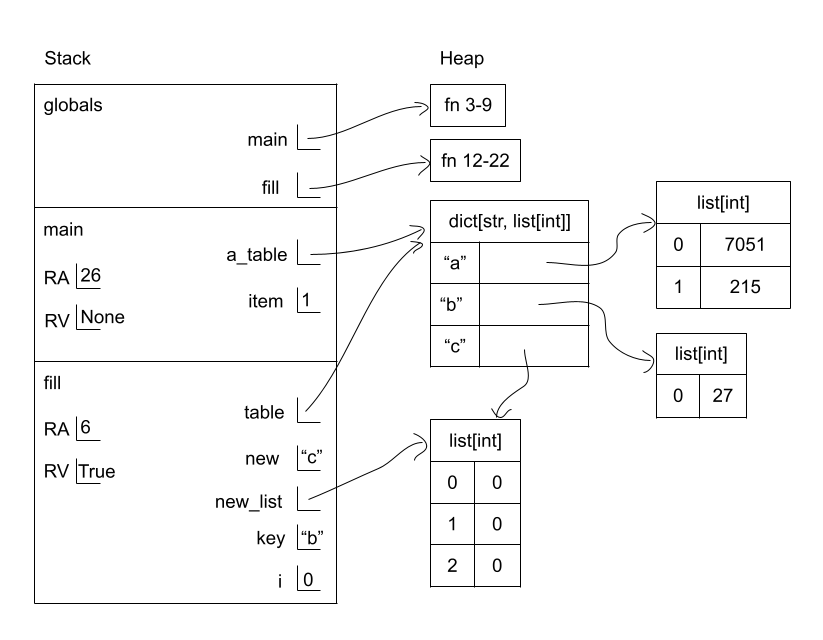
- No. As the loop iterates over
a_table["c"], which is a list,itemis assigned the same value as each value in the list. So for example, in the first iteration of the loop,itemhas the same value asa_table["c"][0], but adding 1 toitemdoesn’t changea_table["c"][0]. - 2
Function Writing 1
One possible solution is shown below, but there are multiple solutions!
Global Variables
- Output:
5
5- Line 3
- 1
- Line 10